Regulatory Reporting by Small Holding Companies: Common Errors
by Kathy Mai-Vu, Assistant Manager, Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco and Michelle Weatherson, Senior Financial Analyst, Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis
Bank holding companies (BHCs) and savings and loan holding companies (SLHCs), collectively referred to as "holding companies," are required by federal law to file regulatory reports with the Federal Reserve Board. This article highlights some of the common reporting errors on the FR Y-9SP report, Parent Company Only Financial Statements for Small Holding Companies, and discusses how to identify discrepancies between the FR Y-9SP and the subsidiary bank's Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) 041 report, Consolidated Reports of Condition and Income (Call Report), as well as between the FR Y-10 report, Report of Changes in Organizational Structure, and the FR Y-6 report, Annual Report of Holding Companies.1 Holding companies and the Federal Reserve both benefit when these reports are submitted accurately and timely because it minimizes the need for corrections and follow-ups. Also, because the reports are made available to the public, it is important that the data are reliable.
Background and Purpose
BHCs are regulated by the Federal Reserve Board in accordance with the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956 (BHC Act), as amended, and Regulation Y, the implementing regulation for the BHC Act. SLHCs are also supervised by the Federal Reserve as a result of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act amendments to the Home Owners' Loan Act and Regulations LL and MM, the implementing regulations for SLHCs. Many holding companies have less than $500 million in total consolidated assets and are required to file the semiannual FR Y-9SP report. The FR Y-9SP report must be filed by: 1) top-tier holding companies with less than $500 million in total consolidated assets; 2) each holding company within a tiered organizational structure in which the top-tier holding company has total consolidated assets of less than $500 million; and 3) subsidiary holding companies of Employee Stock Ownership Plan holding companies with less than $500 million in total consolidated assets.
Information collected on the FR Y-9SP report is used to assess and monitor the financial condition of parent holding companies. In fact, the FR Y-9SP report is in the FR Y family of holding company reports that serves a variety of needs for the Federal Reserve and enables analysts and supervisory staff to:
- Analyze holding companies' overall financial condition
- Review holding companies' performance and conduct pre-inspection analysis
- Review applications for mergers and acquisitions
- Identify potential financial trends or problems
The FR Y-9SP report is completed as of the last calendar day of June and December and must be filed with the Federal Reserve 45 days after the quarter ends. Shifts in reporting status occur when a holding company reaches $500 million as of June 30; generally, this requires the filing of the FR Y-9C report, Consolidated Financial Statements for Holding Companies, and the FR Y-9LP report, Parent Company Only Financial Statements for Large Holding Companies, beginning March 31 of the following year. However, if the $500 million threshold results from a business combination, the change in reporting to the larger series would occur as of the next calendar quarter.
The Federal Reserve received 4,095 FR Y-9SP reports for the December 31, 2012, reporting period. Figure 1 shows a breakdown, by Federal Reserve District, of holding companies that file the FR Y-9 series of reports.
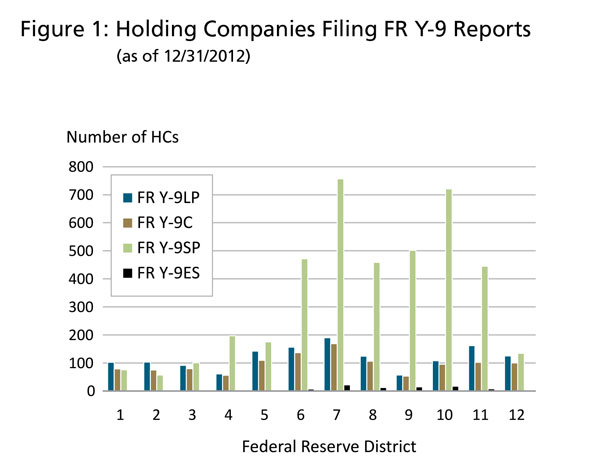
Data Analysis and Common Reporting Errors
The FR Y-9SP report collects basic financial data on a parent-only basis in the form of a balance sheet, an income statement, and a schedule for certain memoranda items. It must be prepared and filed in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The equity method of accounting should be used when accounting for investments in subsidiary banks, as well as nonbank subsidiaries, associated companies, and corporate joint ventures in which the holding company exercises significant influence.
Although the FR Y-9SP report is not complex in terms of the data collected, some accounting and reporting issues are common to FR Y-9SP reporters. Because the report is filed only twice a year, these issues seem to resurface from time to time. To ensure the accuracy of reported data, Federal Reserve analysts perform period-to-period consistency checks, paying particular attention to unusual fluctuations. Analysts also verify that the data and any edit explanations provided are consistent with accounting rules and reporting interpretations. In addition, analysts often perform extended editing beyond analysis of the FR Y-9SP report data by cross-referencing other sources, such as the Call Report, structure reports, and Securities and Exchange Commission reports, if available.
Reconciliation of the FR Y-9SP Against the Call Report
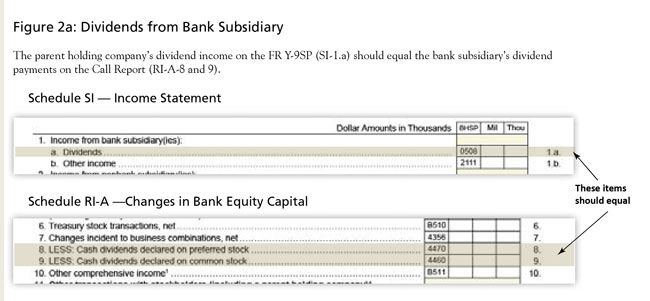
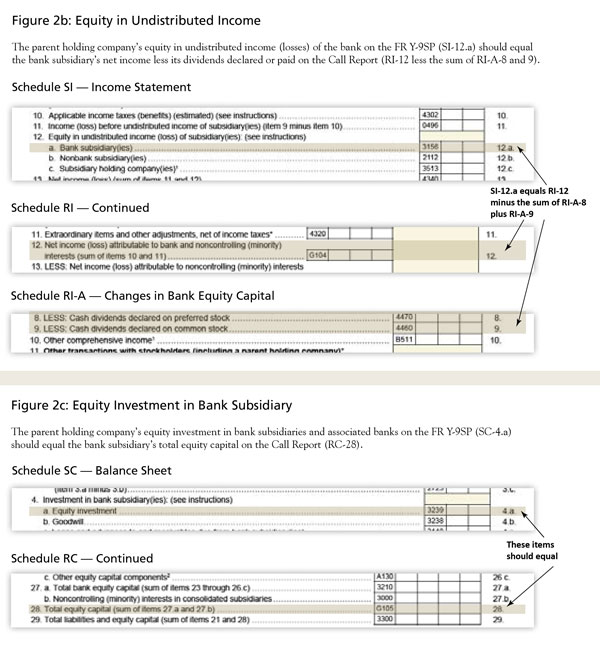
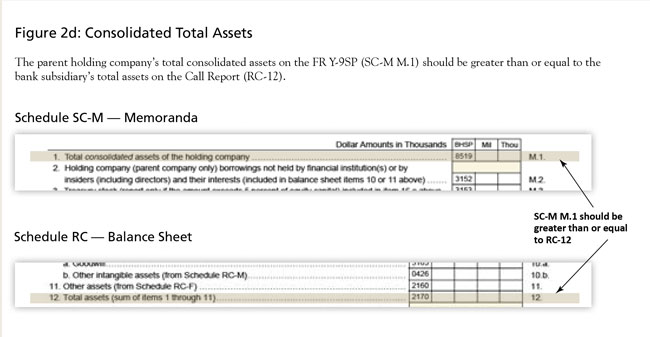
When the FR Y-9SP is reconciled against the Call Report data, analysts are able to uncover discrepancies and request revisions from the reporters. These examples assume the holding company owns 100 percent of the subsidiary's equity. In cases of less than 100 percent ownership, a pro-rata calculation is used to verify accuracy for the Schedule SI (income statement) and Schedule SC (balance sheet) items noted (Figures 2a-c). As shown in Figure 2d, for item 1 (total consolidated assets of the holding company) of Schedule SC-M (memoranda), the subsidiary bank's total assets, plus any parent-only assets, should be reflected. Line items that should reconcile properly are also noted.
Reconciliation of FR Y-9SP Against FR Y-10 and FR Y-6 Structure Reports
Some line items on the FR Y-9SP report provide for a cross-check with the FR Y-10 and FR Y-6 structure reports. As shown in Figure 2c, Schedule SC, line item 4.a discloses the holding company's equity investment in its subsidiary bank. Because the equity method of accounting is used, Reserve Bank staff can reconcile this figure against the subsidiary bank's Call Report. A discrepancy between the FR Y-9SP report and Call Report data may indicate that an FR Y-10 report should be filed to report a change in ownership percentage.
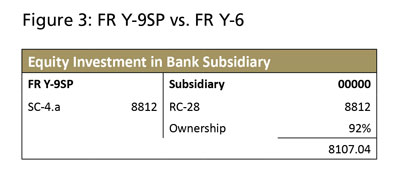
As noted in Figure 3, equity investment (SC-4.a) is calculating to 100 percent of the bank's equity capital (RC-28). However, ownership structure from the parent holding company's most recent FR Y-6 report is 92 percent. Follow-up by an analyst is necessary to confirm the percentage and request an FR Y-10 report to report the change in ownership.
In addition, other items on Schedule SC and Schedule SC-M may have balances that indicate the holding company has commenced or ceased some nonbanking activities. Reserve Bank staff cross-check this information with organizational structure data reported on the FR Y-10 report. If the nonbanking company or activity does not coincide with the FR Y-9SP report data, a follow-up call is made to request an FR Y-10 report or revisions to the FR Y-9SP report.
Other Common Reporting Errors
As shown in Figure 4a, the cash dividends reported in SI-M.1 should include dividends from both common and preferred stock.
As noted in Figure 4b, the respondent should answer yes or no to the question and provide the auditor information as requested. This section should be left blank for June but should be completed for December.
As noted in Figure 4c, SC-M.14 must always be completed and no portion should be left blank. The respondent should answer yes or no to the question and provide the FR Y-10 contact information as requested. If a top-tier holding company reports no to SC-M.14, analysts will follow up with the company to confirm whether an FR Y-10 report should be expected to record a change(s).

Upcoming Reporting Changes
SLHCs with less than $500 million in total consolidated assets that currently report on FR Y-9SP will soon be subject to consolidated regulatory capital requirements. A proposal to amend the FR Y-9SP form by adding a new schedule SC-R, Regulatory Capital, was published for public comment in the Federal Register on August 12, 2013.2 Additionally, evolving accounting changes could also result in a more complex FR Y-9SP report for all holding companies. Therefore, additional analysis of the data will be implemented to ensure reporting accuracy, as needed.
Outreach Efforts and Reporting Aids
The Regulatory Reporting and Structure Reporting sections at the Federal Reserve Banks and the Board work together to ensure that accurate and timely data are collected in accordance with the regulations and reporting instructions. Many Federal Reserve Districts conduct outreach programs with reporters to educate holding companies and to help ensure more accurate reporting, particularly when there are changes to reporting forms. Some of these outreach efforts include Ask the Fed sessions and webinars on various reporting topics that community banks are invited to attend.3 Some Districts also provide checklists or worksheets to aid reporters in completing the reports.
The current FR Y-9SP form is straightforward. With periodic accounting rule and report form changes, it is to the holding companies' advantage to understand the reporting issues highlighted above and collaborate with their local Federal Reserve Bank analysts to resolve any confusion related to them. Staff members at the Federal Reserve Banks are available to assist holding companies with any reporting questions.
Back to top
-
1
Reporting forms and instructions are available at www.federalreserve.gov/apps/reportforms/default.aspx.
-
2
See the Federal Register at
www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/press/foiadocs/2013/20130812/foia20130812.pdf.


-
3
See Ask the Fed at
www.stlouisfed.org/BSR/askthefed/.

